Despite being harshly criticized over several decades in the past, you might wonder why network marketing is still a multi-million-dollar business industry. There are numerous legal and ethical regulations governing multi-level marketing (MLM). Nonetheless, the model continues to remain lucrative for the 120 million (and counting) people worldwide involved in the direct selling industry.
This unique behaviour has prompted various studies and research to be conducted on understanding the psychology behind network marketing. It primarily involves understanding and analysing two driving factors of the business – motivation and persuasion.
Table of Contents
Motivation
As you already know the basics of the MLM model, it must be clear to you that the flesh and blood of an MLM business are its distributors. They establish the market presence, drive sales, promote the brand, build trust and transparency, onboard, train, and recruit new distributors, and so much more! Hence, it is of utmost importance that the distributors start, stay, and remain motivated.
Inorder to do that, Network marketing ventures need to ensure distributors aren’t wasting time on repetitive tasks. Integrated MLM Software automates operations and provides valuable data on distributor preferences and behaviour. This data can be used to create a motivating, error-free reward system.
Now, let’s understand the factors other than fair compensation, that drives and governs the distributor motivation:
- Self-Determination Theory posits that humans possess three fundamental psychological needs—autonomy, competence, and relatedness—which serve as essential drivers of personal growth and development.
- A part of this notion, is the ‘Goal Contents Theory’ which defines two types of Motivation
1. Extrinsic Motivation:
This is the motivation to build one’s image. Extrinsic goals motivate people to garner money, material possessions and popularity.
- This is also attributed to consumerism and compulsive buying due to Fear-Of-Missing-Out.
- MLMs are promoted as a route to “financial freedom” and elevated social status by advancing up the MLM business hierarchy.
- The most enticing prospect of MLM lies in its low investment, easy entry, extensive market reach, and valuable entrepreneurial experience, offering a highly rewarding opportunity.
2. Intrinsic Motivation:
It is defined as the satisfaction achieved by doing the activity rather than the rewards flowing from it.
- MLM training and courses foster distributor personal development.
- Deep relationships and social impact in MLM bring meaning to distributors’ lives.
- Distributors enjoy autonomy that comes with the job, empowering them in life decisions.
- Flexible schedules promote work-life balance, attracting many to the industry.
- Many MLM Businesses promote ethically and environmentally sustainable products as innovative products fit the MLM model. Working for socially responsible brands promotes self-esteem in the distributors.
- Even physically challenged individuals can excel as distributors due to their social presence.
- Most MLM companies greatly appreciate the extraordinary efforts made by the distributors. Hence, appreciation and recognition from MLM companies motivate distributors
Now let’s dig into what motivates the consumers or new recruits to buy the products or join the company as distributors respectively.
The reason why masses are attracted to the MLM business depends on several ‘cognitive factors’.
1. Rational v/s Intuitive:
- People who are mostly attracted to MLMs are people who think intuitively rather than those who analyse rationally. People who generally take swift decisions based on gut-feeling and emotions are attracted towards MLMs. Those who deliberate extensively tend to remain sceptical about MLMs.
- Though intuitive decision makers are most attracted towards an MLM, there are many other factors that finalize their decisions including the depth of their financial knowledge.
2. Thought-action fusion:
- People who believe in ideas such as the ‘pseudo-scientific’ Law of Attraction, which holds that thoughts create one’s reality, are attracted to MLMs.
- These notions further solidify people’s belief that purchasing the hyped product or joining the business will solve all their problems, motivating them to agree with the business.
3. The Religious Influence:
- Economic research such as Bosley & Knorr, 2018, clearly delineates the increased likelihood of people participation in direct selling schemes from regions with high density of religious groups.
Persuasion
Persuasion, or the art of influence, must be distinguished from manipulation. Manipulation involves unfairly and dishonestly attempting to push or even control someone’s decision to a desired outcome, whereas persuasion has a far more positive connotation. In persuasion, an attempt is made to guide someone towards a decision while understanding and respecting their autonomy and boundaries.
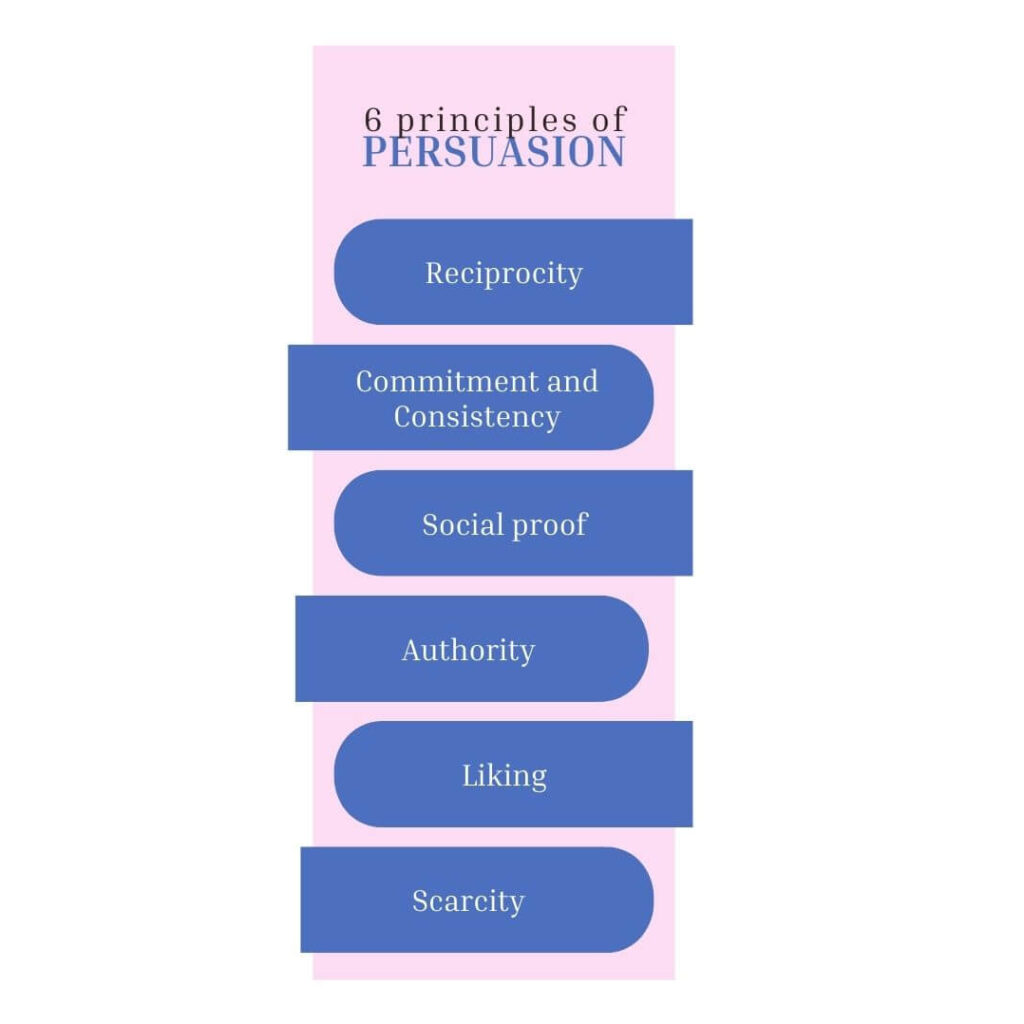
There are 6 principles of persuasion according to the celebrated Psychologist Dr. Robert Cialdini.
- Reciprocity : By offering value and services to consumers and prospective recruits, such as free samples, resources, guidance, and mentoring, people will feel obliged to return the favour by purchasing the product or joining the company.
- Commitment and Consistency: Once the participant commits to an action such as attending a webinar or trying out a freebie, chances are they will continue the commitment, like joining the team.
- Social proof: Show a before-and-after picture of someone whose life was physically or financially transformed by the product or services of the company. Proof builds trust. You can also borrow and leverage credibility by getting endorsed by famous people.
- Authority: Strengthen your credentials as an expert in the subject. For example, “As a nutritionist, I can guarantee that naturally sourced supplements are always better than synthetic ones.”
- Liking: Building genuine relationships with trust, honesty, and reliability will help in aligning the objectives of the consumer with yours. The “Feel-Felt-Found” technique can be used where you actively listen to the participant, reciprocate their concerns with understanding, and showcase reliable and relatable success stories. People tend to show increased trust and commitment in groups. Hence, try to build a community of like-minded individuals whose interests align with the company’s market.
- Scarcity: This is a way of persuasion to capitalize on participants’ fear of missing out. Scarcity through limited-time offers amplifies the value of the product. Deadlines create urgency to obtain the value. However, scarcity and urgency must be used with responsibility and transparency to build long-term relationships.
Avoid These Pitfalls
- Motivation and persuasion are in no way manipulation. The power of influence must be leveraged, but responsibly. Disclose average income earned, product market performance, quality of products or services offered, and all the risks associated.
- Aggressive recruitment in the name of commissions may lead to market saturation and an inability to find consumers. Persuading people to join the company based on flimsy promises may backfire in the end. Recruiting must be paced and sustainable, along with adhering to legal and ethical regulations. To keep a tab on distributor activity, MLM businesses can resort to the best MLM software in the market that provides a snapshot of users’ recent activities and financial transactions to help stay updated and accountable.
- While aspirational stories showing luxurious cars and a lavish lifestyle can be persuasive, product quality and benefits, personal development associated with joining the company, etc., must be highlighted to sustain a long-term trustworthy relationship
- Provide customers with full details and information rather than exploiting their confirmation bias due to their selective trust in success stories. Studies have proven that although accurate disclosure of average income was made, while it reduced income expectations, it did not reduce motivation to join the company.
Conclusion:
The psychology of MLM is balancing appeal and influence through carefully using factors such as motivation and persuasion. By carefully educating the customers and ensuring fact-based decision making, an MLM company can sustainably establish their market presence in the long-term.